“Comparing Arrays in JavaScript: Different Methods and Examples”
Methods
In JavaScript, there are several ways to compare arrays. The choice of method depends on the specific requirements of your comparison. Here are some common types of array comparison in JavaScript:
1. Shallow Equality Comparison
2. Deep Equality
3. Comparison
4. Set Comparison
5. Sorting and Comparison
6. Length ComparisonShallow Equality Comparison
This type of comparison checks if two arrays have the same elements in the same order. It uses the strict equality operator (===) to compare each element of the arrays. If the order and values of the elements match, the arrays are considered equal.


Deep Equality Comparison
Deep comparison involves checking if two arrays have the same elements regardless of their order or nested structure. It requires comparing the values of nested objects or arrays recursively. Libraries like Lodash or Underscore.js provide functions like isEqual() that perform deep equalitycomparisons.

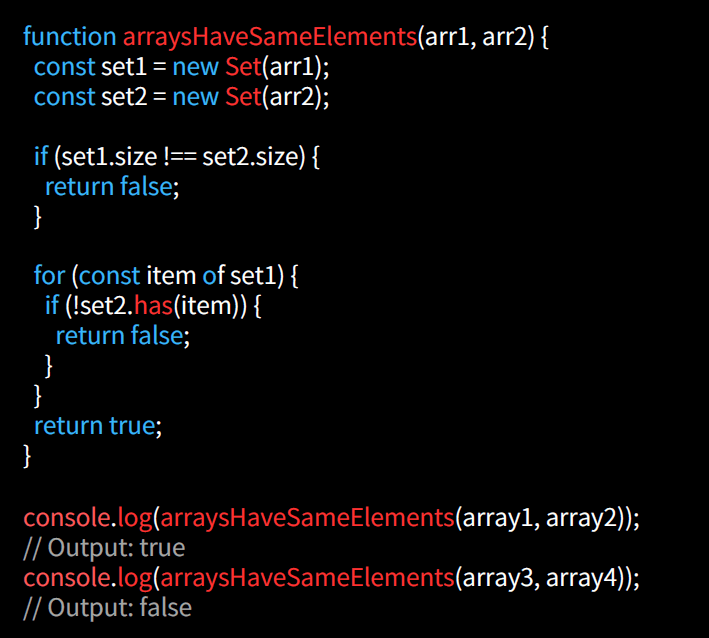
Set Comparison
Comparing arrays as sets involves checking if they contain the same unique elements, regardless of order. The Set object in JavaScript can be used to convert arrays to sets and perform set operations like subset, superset, or equality comparisons.
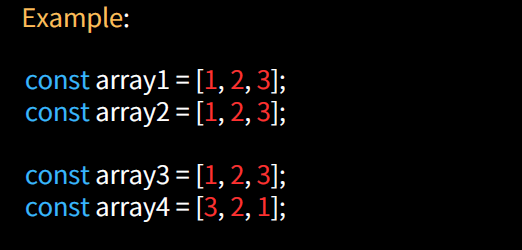
Sorting and Comparison
This type of comparison involves sorting the arrays and then comparing them element by element. It checks if two arrays have the same elements regardless of order. If the arrays have the same length and their sorted elements match at each index, they are considered equal.
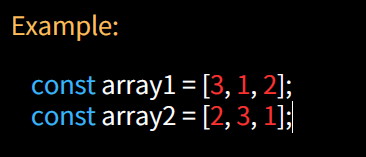
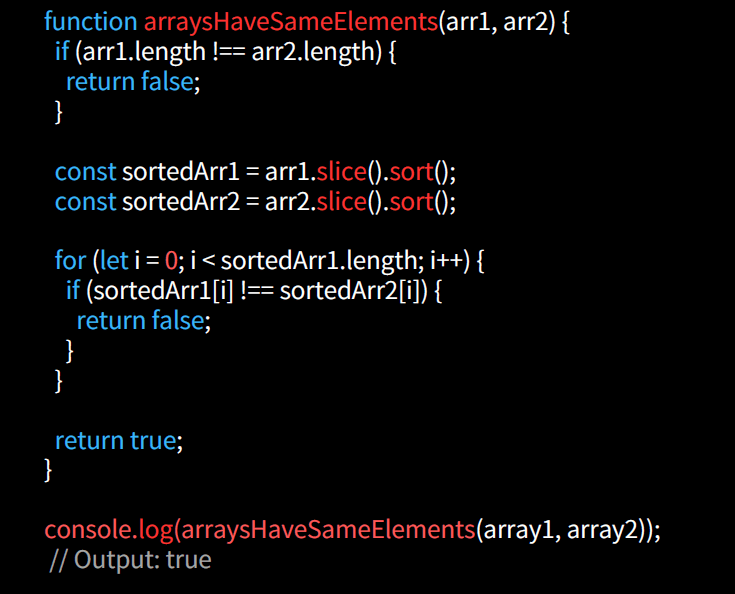
Length Comparison
Simple comparison of the lengths of two arrays to check if they have the same number of elements. This method does not consider the actual values of the elements, only their count.